Source:- thehindu.com
Cases of acute encephalitis syndrome have seen a spike in Muzaffarpur this year, already claiming more than a hundred lives. Jacob Koshy reports on the appalling state of health care in Bihar, even as the debate on what is causing the deaths rages on
For three days, Bihari Mahato and Shyam Babu Saha’s families have shared a hospital bed. The two daily-wage labourers, who have had to give up work for three days, haven’t exchanged a word, though they have much in common. Both have a boy and a girl each. And their children are battling for life.
Sundar, Mahato’s three-and-a-half-year-old son, is naked, emaciated, delirious and has a distended stomach. Himanshi, six months old and in a striped shirt and shorts, looks bigger and healthier than Sundar. She sleeps longer — fitfully, her mother Vimla says. Both families are from different districts of Bihar. Mahato is from Muzaffarpur and Saha is from Sitamarhi district. Their children were suddenly taken ill. When the children were convulsing and feverish, they were rushed to the Sri Krishna Medical College and Hospital (SKMCH) in Muzaffarpur. The doctors noted that their blood sugar had dropped precipitously.
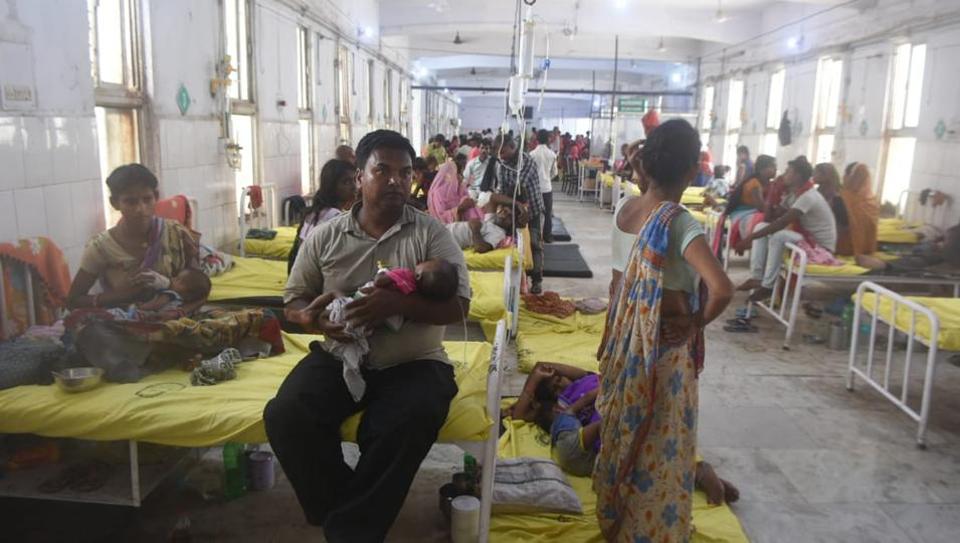
Both children are being given dextrose saline (a sugar solution often administered intravenously), but their parents are nervous. “The fever has subsided but it keeps returning,” says Saha. “The doctors aren’t paying us much attention.” But that’s a quibble given that many other ailing children are sprawled out on mattresses on the floor. Amidst peeling plaster, strewn banana peels, stomping doctors, nurses, journalists and television crew, the children’s ward at SKMCH is symptomatic of the confusion and panic that has gripped Muzaffarpur since early June.
The floor above the general ward is home to the Intensive Care Units (ICUs). Each of the five ICUs has eight beds. Not one of the beds has fewer than three children hooked to bleeping monitors and intravenous lines. Unusually for an ICU, there’s little restriction on non-hospital staff shuttling in and out, but unlike the squalid paediatric wards below, there are no patients sprawled on the floor. The floor is clean, the air-conditioners work, the nurses are extra vigilant, and yet here’s where death lurks around the corner.
Season of trouble
There is a protocol for doctors. As soon as children are wheeled in, they are monitored for fever, convulsions and signs of confusion or loss of consciousness. “What I’ve seen is that several children are brought too late. Unfortunately we lose them,” says J.P. Mandal, a resident doctor at SKMCH. Between June 1 and 17, 312 children were admitted to the hospital under the umbrella diagnosis of acute encephalitis syndrome (AES). According to the Bihar health department, 85 died. The bulk of the dead, 48, were children aged three to seven. Twenty-nine children were less than three years of age. As of June 21, 104 of the 424 children admitted since January 1 had died. Encephalitis, which refers to an inflammation in the brain due to a viral or bacterial attack, causes fever and almost never a drop in blood sugar. In the current epidemic, as well as in previous ones in Muzaffarpur, the doctors have marked cases of and deaths by hypoglycaemia (drop in blood sugar), which is unusual.
While Bihar loses hundreds of children to AES every year, there were sharp spikes in 2012 and 2014, when 395 and 372 children, respectively, lost their lives. Through the years, AES cases have been reported from several districts in Bihar: Gaya, Patna, Aurangabad, Saran, East Champaran, Sitamarhi and Vaishali. Government figures show that the peak years of 2012 and 2014 saw Muzaffarpur account for 35-40% of hospital admissions. While this year’s incidences and deaths are fewer in comparison, the season of trouble is far from over. The outbreak in 2012 took place between May and November. In 2014, it was from May to July. There’s no saying how long the current outbreak will last. A common refrain among district administration officials and some doctors is that the yearly outbreak ceases in intensity soon after the monsoon rains begin in Bihar. Why is that? Nobody ventures an explanation.
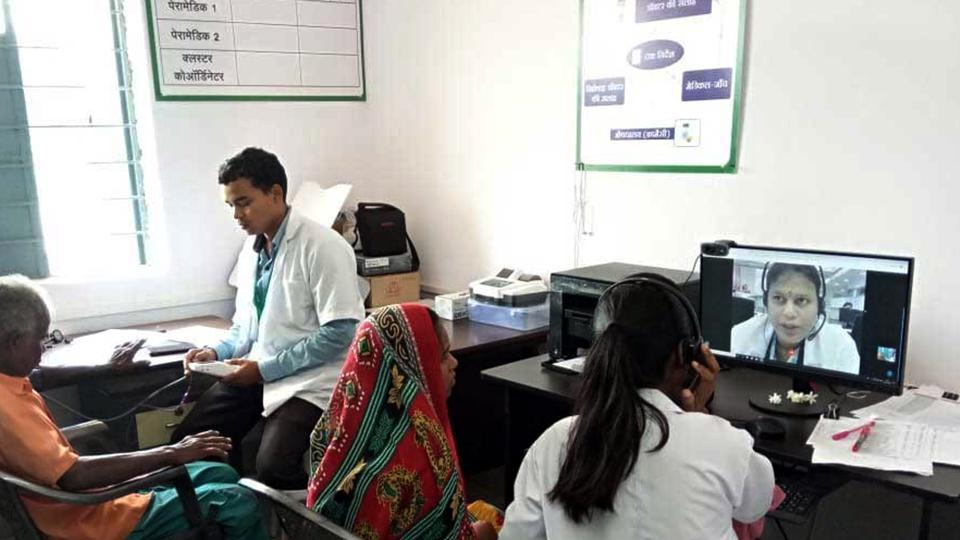
Sanjay Kumar, the State’s top civil servant in charge of health, says he cannot quite put a finger on a “single, determining factor” that is responsible for 2019 turning out to be a bad year. It could be the ongoing heatwave — several parts of Patna, Gaya and even Muzaffarpur have recorded temperatures in excess of 4-5°C over what’s normal for this time of the year. At least 80 people have succumbed to the heatwave. “The added heat and humidity could have made young children particularly susceptible to dehydration,” he reckons. “It could also be an infectious disease. It could also be because of children eating litchis.”
Kumar says all the children who are admitted belong to the lowest socio-economic rung; there are no instances of infection in cities or even semi-urban localities. He emphasises that the government had been prepared this year too, like in the past, for the outbreak. It stocked up and supplied oral rehydration solution, ensured that medicine and equipment were provided at medical colleges and district health centres, and conducted public awareness campaigns about the imminent outbreak. However, he admits that the district’s key referral hospital, SKMCH, wasn’t equipped to deal with the deluge of patients. “This year will be a turning point. The bed capacity will be increased to 1,500 and we will have a virology lab [to better investigate vitals of patients and determine disease causes].”
Debating the litchi link
Arun Shah, a paediatrician and private practitioner who has been working in the city since 1984, insists that the spike in AES cases and in fatalities is a result of malnourished children suffering brain damage after eating litchis, particularly unripe or overripe ones. In a 2014 paper, Shah and virologist T. Jacob John had argued that the children in Shah’s clinic in Muzaffarpur were found to have extremely low blood sugar levels and signs of brain damage. While viral or bacterial infections that cause encephalitis (an inflammation of brain cells due to an infection) were well known in Muzaffarpur and neighbouring districts, many of them were taking sick and dying due to encephalopathy (brain damage, in this case, due to an environmental toxin). In 2016, a detailed investigation, published in The Lancet Global Health by the National Centre for Disease Control, India, and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, found “confirmation” that litchis contained a chemical called methylene cyclopropyl glycine (MCPG). These are naturally occurring toxins that cause hypoglycaemia and metabolic derangement in children.
When a child is malnourished, her body, having exhausted its reserves of glucose from the digestive tract and the liver, typically turns to fatty acids in biochemical desperation to supply blood sugar to the brain. MCPG, the theory goes, thwarts this mechanism. This can send the brain into hypoglycaemic shock triggering convulsions and, if unaddressed, even death. “But please don’t blame litchis,” stresses Shah. “It is the pride of Muzaffarpur.”
At a press conference two years ago, to underline that the litchi fruit was only a triggering factor and sickened only malnourished children, Shah and John ate a bowlful of the fruit in front of television cameras to emphasise that it was malnutrition, and not the fruit, that was the dominant cause of the disease. Shah is unambiguous that the children are suffering because the government didn’t do enough. The recently concluded Lok Sabha election distracted the government from adequately preparing for the outbreak, he says. In 2016, he was part of a government-constituted committee that prescribed guidelines: Children shouldn’t be allowed to skip their evening meal, they should avoid stepping out in the heat, and local public healthcare centres must stock up on anti-convulsion drugs as well as dextrose. These were adhered to in 2017 and 2018. And that’s why there were relatively fewer reports of AES, he argues.
While encephalitis outbreaks in Uttar Pradesh’s Gorakhpur were due to other causes, and children from Muzaffarpur and neighbouring districts have battled viruses such as the Japanese encephalitis virus, the large-scale litchi cultivation in Muzaffarpur, which contributes about 40% of the State’s litchi production, “can’t be ignored as a triggering factor,” he points out.
At SKMCH, several parents of the ailing children are categorical that their children did not eat litchis. The authors of The Lancet study found that two-thirds of children who were sick had eaten litchis. “We work in the fields and there are litchi orchards aplenty where we live,” says Indal Paswan, whose two-and-a-half-year-old son is prostrate on a hospital bed. “But this boy isn’t capable of plucking fruit on his own. We do feed him some fruit as well as other food but we don’t starve him.”
Mandal is insistent that there is a virus or some biological agent that is responsible for the recurrent outbreaks. He scoffs at suggestions of the litchi’s complicity. Children who were brought to the hospital were “poor but not classically malnourished,” he says. If malnutrition and litchi consumption were the causes, then there ought to have been a fairly constant number of deaths every year. This has not been observed, he says. “A peak and an ebb in cases and deaths is what we see. And that’s more typical of a biological agent.”
That no virus or bacteria has been isolated yet in Muzaffarpur is because the hospital lacks adequate facilities to collect tissue and blood samples from patients and preserve them adequately for examination. “I’m confident that at some point this will be found and there will be no mystery,” Mandal says. The focus of treatment, he adds, is to ensure that convulsions are brought under control and blood sugar levels are restored.
What Shah and Mandal do agree on is that the vast majority of deaths could have been prevented if the children had made it to a hospital on time. The most important medicines were easily available, and most of the primary health care centres were well stocked and equipped to deal with AES cases.
No time to grieve
Yet, four-year-old Mohammed Jahid lost his life. Until he fell sick, Jahid had spent his days playing with his older siblings and cousins in the village of Bishnupur Chand, Musahari. His home was a single room thatched hut that did not have a toilet. His and his cousins’ houses lay at the edge of an orchard that had several rows of tall, stout litchi trees. In June, there were only a few fruits that clung to the trees. Most had been plucked and carted away for sale by the owner of the orchard who lives in Patna. “He didn’t show any signs of illness. He had a fever for two days,” recounts Jahid’s aunt, Asha Khatoon. “We took him to a private doctor nearby.” One night, Jahid became delirious, and his father Mohammed Idris rushed to get an autorickshaw to take him to a hospital. He didn’t find one immediately as the roads had been dug up. When they made it to SKMCH, Jahid was immediately taken to the ICU, but he didn’t survive beyond three hours. A day after burying Jahid, Idris was away to find work as a daily-wage labourer. There were still two boys, two girls and a wife to feed.